Unit 2. We take care of our senses.
Index
1. We understand what is sensitivity and how it works
2. We learn about the nervous system and its organs.
3. We learn about how the different senses work and their main organs .
4. We develop healthy habits to take care of our systems.
Vocabulary.
- Brain
- Cerebellum
- Nerve
- Peripheral nervous system
- Central nervous system
- Response
- Skeletal system
- Muscular system
- Taste buds
- Brainstem
- Spinal cord
1. What is sensitivity?
Sensitivity is one of the life processes. We can say that sensitivity is how we interact with the world through our senses. First, we receive a stimulus that is detected by one of our senses. That information is sent to our nervous system that process the information and give a response. Finally, our muscular and skeletal systems react to produce that response.
The nervous system has two main parts:
- The central nervous system is made up of the brain and spinal cord.
- The peripheral nervous system is made up of nerves that branch off from the spinal cord and extend to all parts of the body.
The nervous system transmits signals between the brain and the rest of the body, including internal organs. In this way, the nervous system’s activity controls the ability to move, breathe, see, think, and more.1
The basic unit of the nervous system is a nerve cell, or neuron. The human brain contains about 100 billion neurons. A neuron has a cell body, which includes the cell nucleus, and special extensions called axons (pronounced AK-sonz) and dendrites (pronounced DEN-drahytz). Bundles of axons, called nerves, are found throughout the body. Axons and dendrites allow neurons to communicate, even across long distances.
Different types of neurons control or perform different activities. For instance, motor neurons transmit messages from the brain to the muscles to generate movement. Sensory neurons detect light, sound, odor, taste, pressure, and heat and send messages about those things to the brain. Other parts of the nervous system control involuntary processes. These include keeping a regular heartbeat, releasing hormones like adrenaline, opening the pupil in response to light, and regulating the digestive system.
2.1.Central nervous system
The central nervous system has 2 organs: The brain and the spinal cord.
2.1.1 The Brain
The brain is the most complex part of the human body. Controls the organism and the response to the different stimuli. We can divide the brain into 3 parts:
a) Cerebrum or cortex: The part of the brain that controls the thoughs, memories and process the information.
b) Cerebellum: Is the part of the brain that controls movement and balance.
c) Brainstem: Controls the internal organs.
The spinal cord is the main pathway for information connecting the brain and peripheral nervous system. In humans, the spinal cord is a continuation of the brainstem.
2.2.Peripheral nervous system
Our peripheral nervous system is that part of your nervous system that lies outside your brain and spinal cord. It plays key role in both sending information from different areas of your body back to your brain, as well as carrying out commands from your brain to various parts of your body.
3.Our senses and sense organs
Senses organs and senses
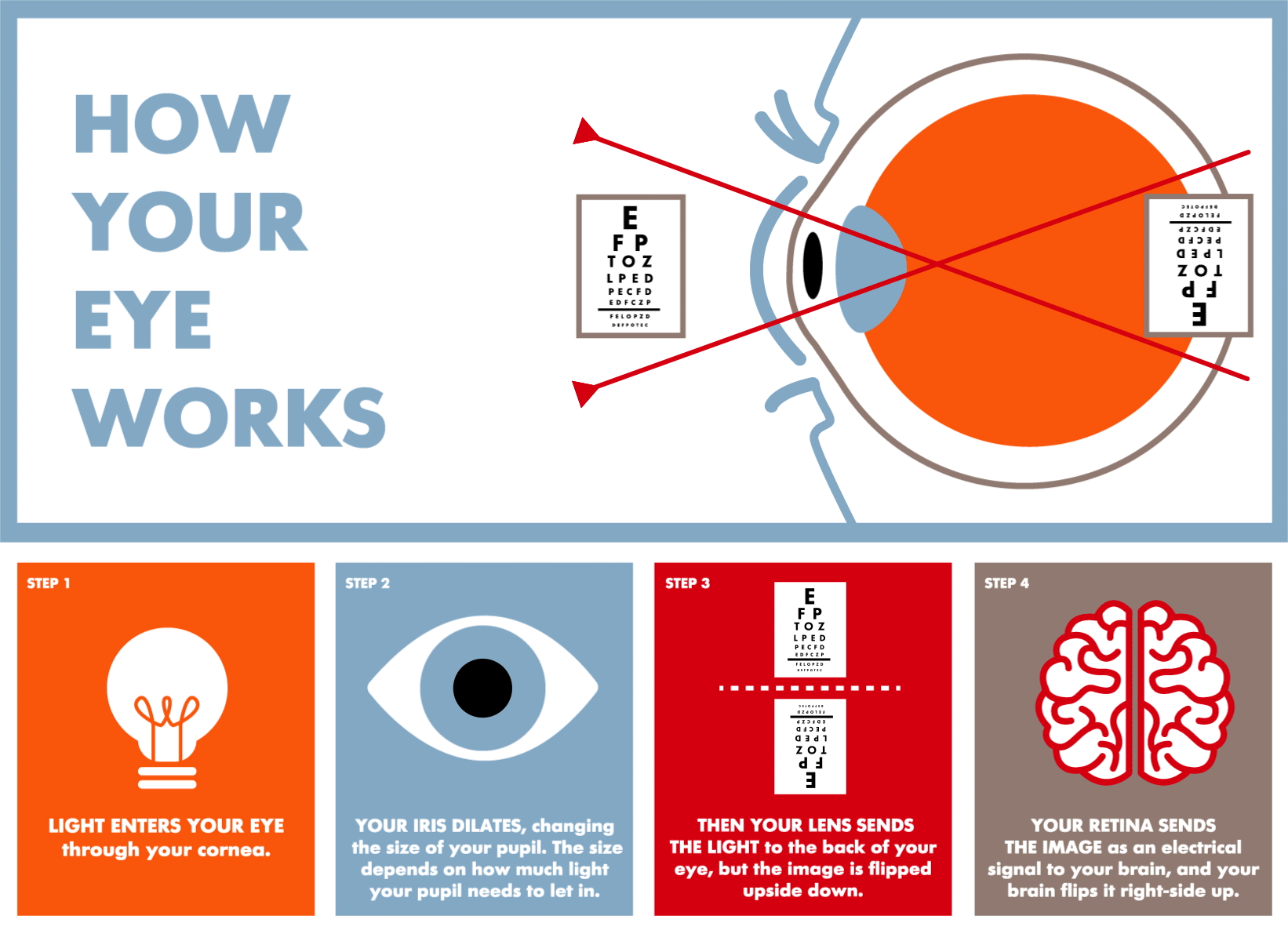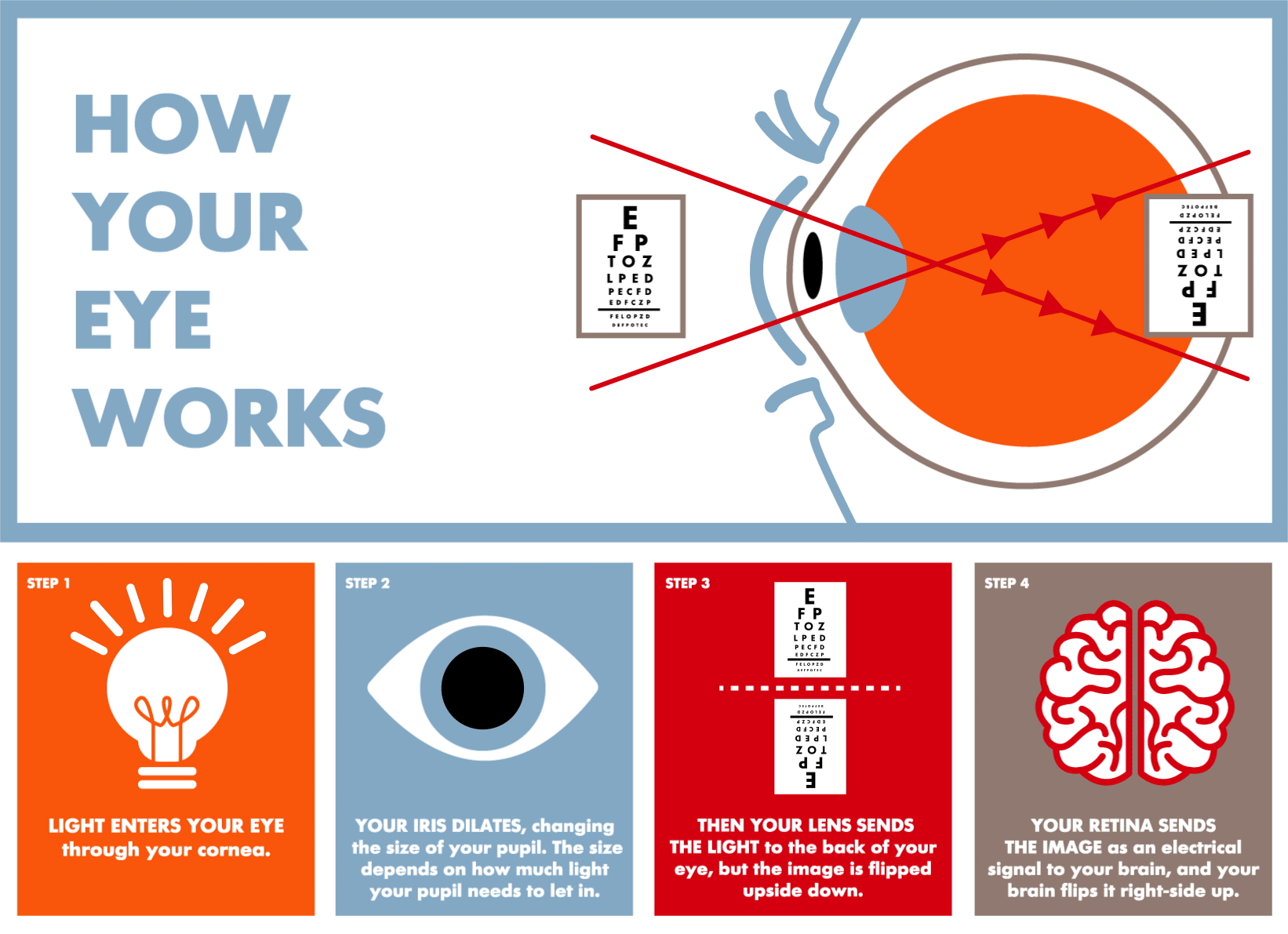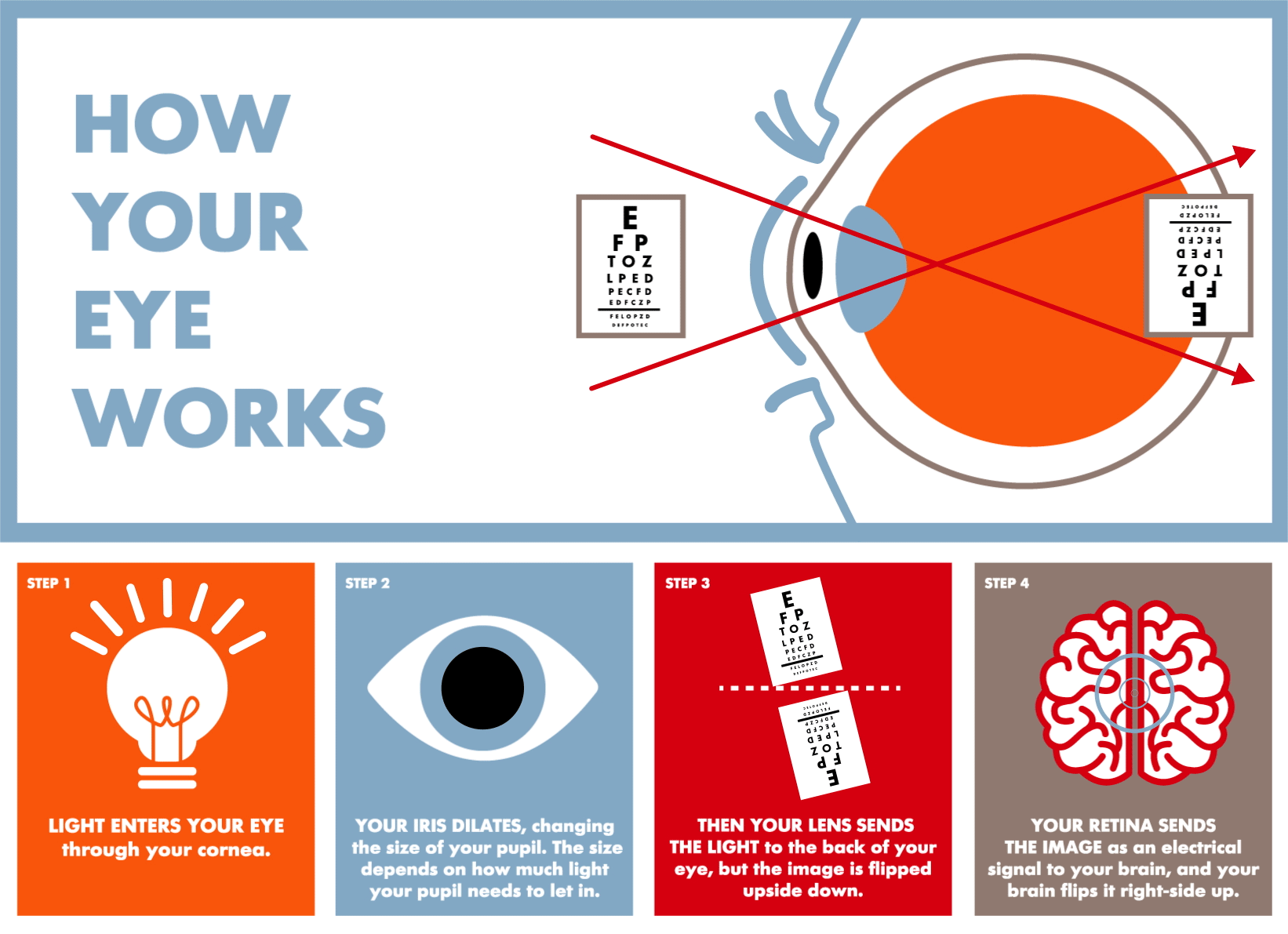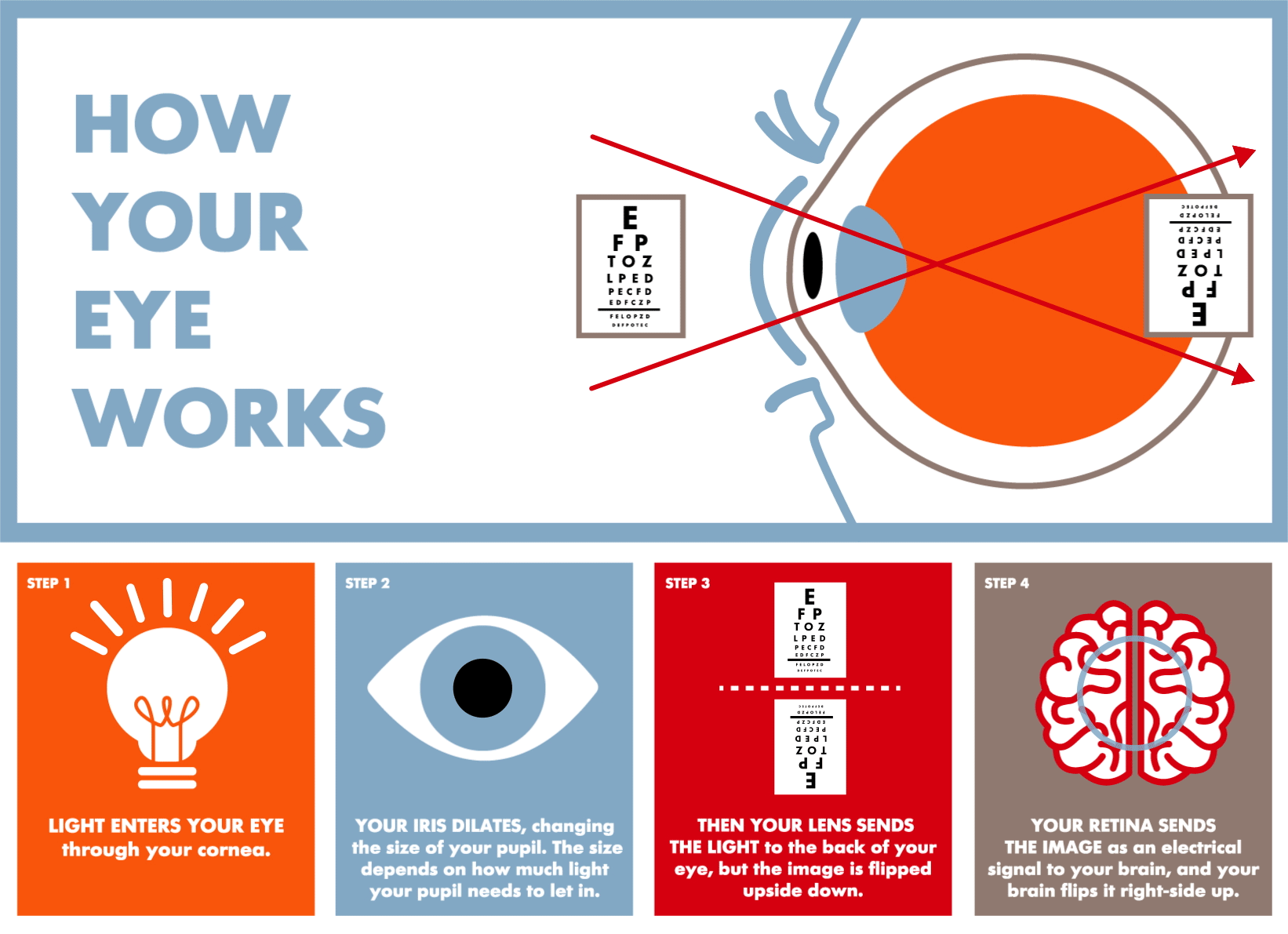
Sight --> Eyes. The eyes are the organs of sight. They detect light and colors, and estimate distances. The information captured by receptors in the retina travels to the brain through the optic nerve. The brain receives and interprets this information.

Hearing --> Ears. The ears are the sense organs of hearing. They detect sounds and their properties, and where this sounds come from. The information captured by receptors in the cochlea travels to the brain through the auditory nerve. The brain receives and interprets this information.

Smell --> Nose. The nose is the sense organ of smell. It detects different smells in the air. The information captured by receptors in the olfactory epithelium travels to the brain through the olfactory nerves. The brain receives and interprets this information.
Touch --> Skin. The skin is the sense organ of touch. It detects temperature, pain, pressure… The information captured by receptors in the skin travels to the brain through the nerves. The brain receives and interprets this information.
Taste --> Tongue. The tongue is the sense organ of taste. It detects different flavours. The information captured by receptors in the taste buds travels to the brain through the taste nerves. The brain receives and interprets this information.



No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario